
Blog
Understanding Biomass: A Renewable Energy Source
17 April 2025
Understanding Biomass: A Renewable Energy Source
Biomass refers to organic material derived from plants, animals, or microorganisms that can be converted into a sustainable source of energy. It plays a critical role in renewable energy systems because it can be replenished naturally through processes like plant growth, making it a cleaner and more circular alternative to fossil fuels.
Biomass encompasses a wide variety of materials, including:
- Wood and wood products: Firewood, sawdust, and wood chips.
- Agricultural residues: Crop waste like corn stalks, rice husks, and wheat straw.
- Animal manure: Rich in organic material, often used in biogas production.
- Food waste: A significant contributor to organic biomass sources.
- Energy crops: Specifically grown for energy, such as switchgrass, miscanthus, sugarcane, and algae.
How Biomass is Converted into Energy?
Biomass can be transformed into heat, electricity, or biofuels through several methods:
- Combustion: Burning biomass directly to generate heat or electricity. This process is used in Evero's Widnes and Lisahally plants.
- Gasification: Evero’s Ince plant uses this process, which converts biomass into a mixture of carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and carbon dioxide (syngas), this syngas can be used for electricity generation.
- Anaerobic digestion: Decomposing organic material in the absence of oxygen to produce biogas (methane).
- Fermentation: Converting plant sugars into bioethanol, a type of liquid biofuel.
- Pyrolysis: Heating biomass in an oxygen-free environment to produce bio-oil, biochar, and syngas.
These processes allow biomass to power homes, businesses, and vehicles, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
Biomass in Action: Sourcing Grade C Waste Wood
Not all biomass is created equal, and at Evero, we’re committed to using only the most sustainable materials.
We specialise in repurposing Grade C waste wood, a material often overlooked in renewable energy conversations.
What is Grade C Waste Wood?
In the UK, waste wood is categorised into different grades depending on its quality.
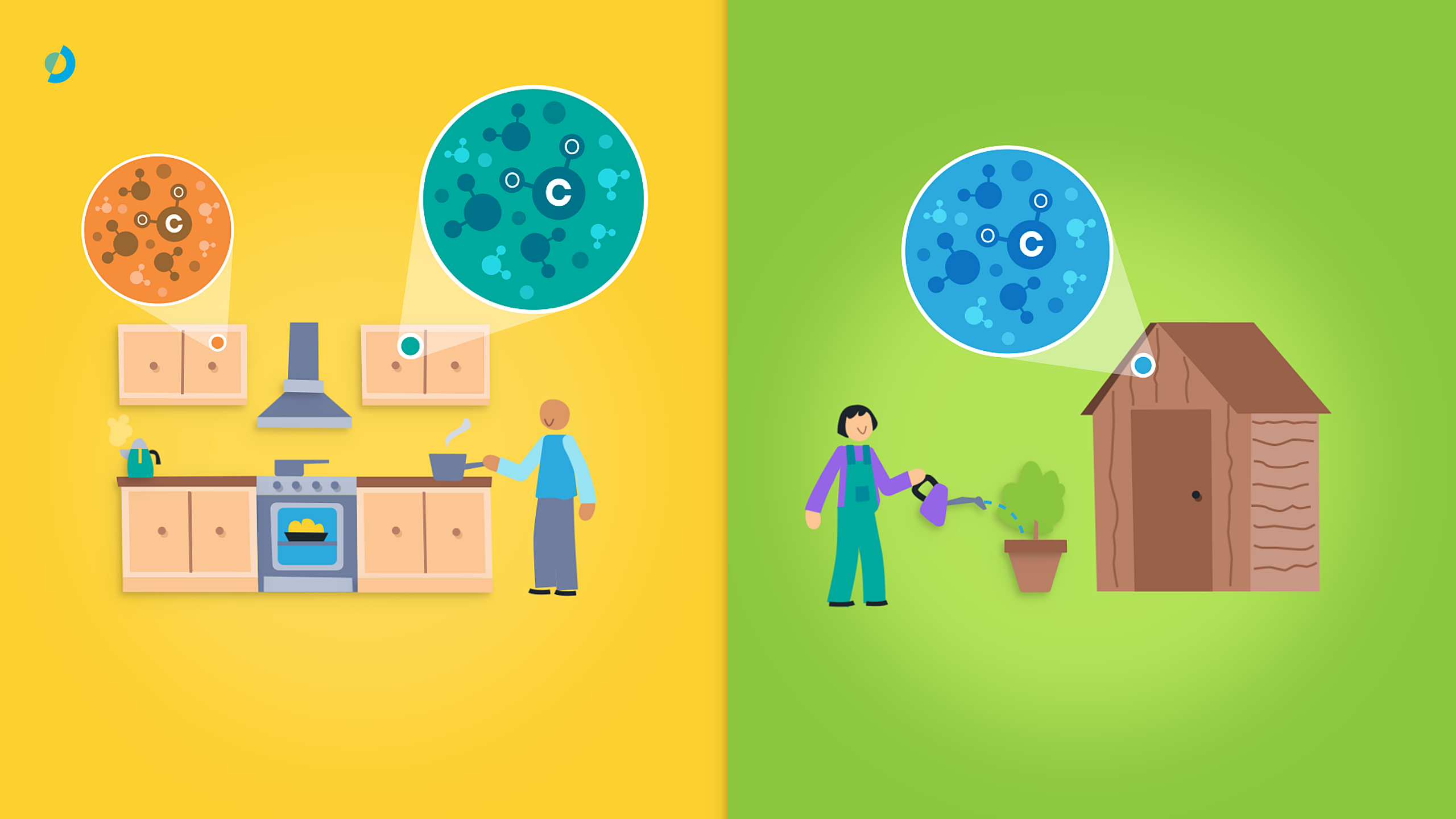
Grade C waste wood refers to processed wood that cannot be recycled or reused in its original form and was previously destined for landfills. By converting this wood into electricity, we ensure that it receives another life and reduce environmental impact by preventing landfills.
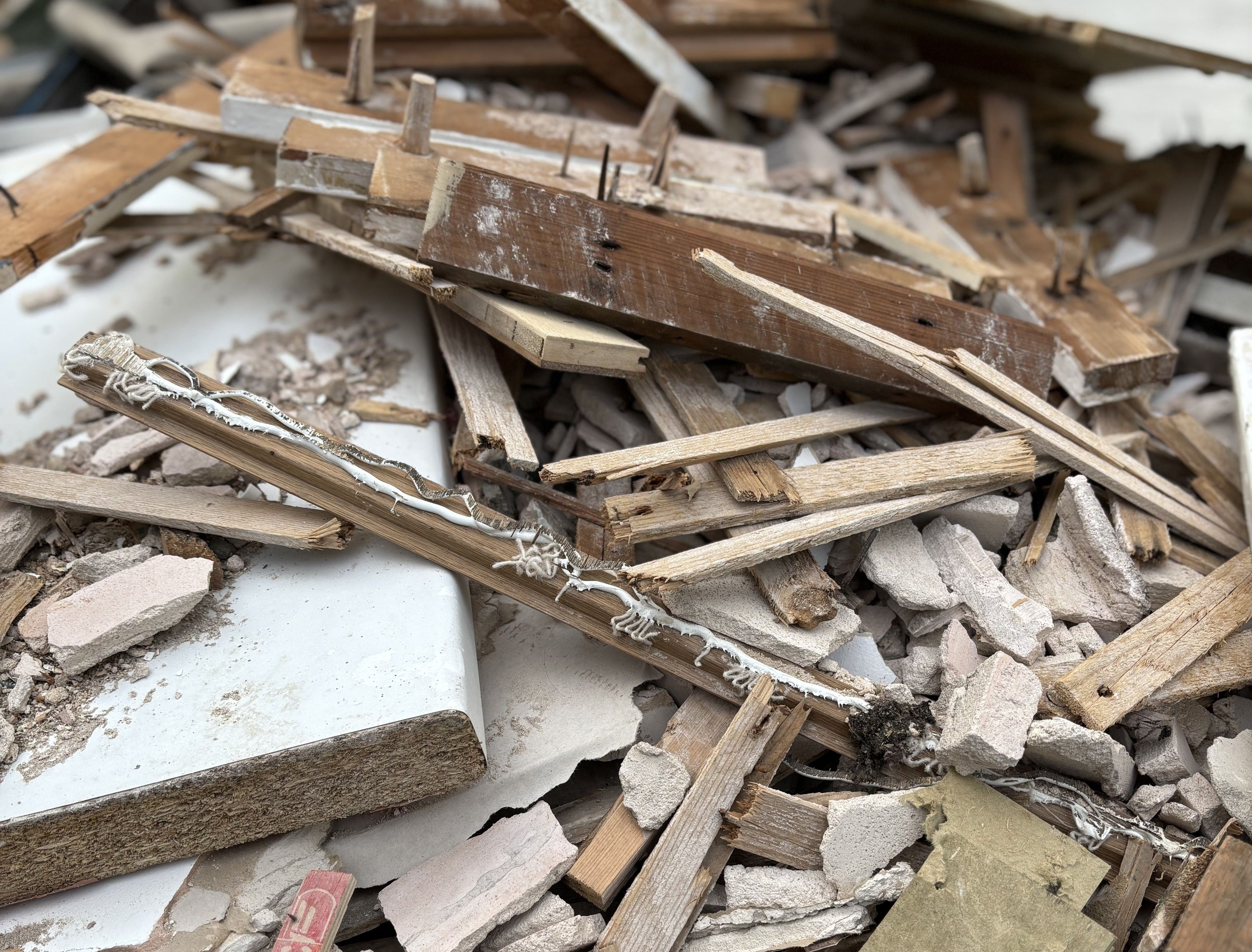
Examples of Grade C Waste Wood
Grade C wood includes non-hazardous treated materials that come from various sources, such as:
Domestic sources:
- Wood from household items.
- Furniture made from MDF, fibreboard and/or plywood.
- Old flooring, and disused kitchens.
Industrial sources:
- Offcuts from construction.
- Furniture manufacturing waste

Why does Grade C Waste Wood Matter?
Grade C wood is unsuitable for recycling due to its coatings, glues, paints, or small embedded materials (e.g., nails, plastics, and rubber). Indeed, it’s often been recycled once already – Grade A and B wood are often recycled to manufacture Grade C wood panelboards.
It’s ideal for use in biomass energy installations. By sourcing this material locally, we not only prevent waste from piling up in landfills but also create sustainable, reliable electricity for UK homes and businesses.
This approach contributes to a circular economy future, where waste becomes a valuable resource rather than an environmental burden.
A Cleaner Future with Biomass
Energy from biomass offers an environmentally friendly, renewable alternative to fossil fuels. At Evero, we’re proud to lead the charge in transforming waste wood into sustainable power, contributing to a greener planet and a cleaner energy system.
By utilising materials like Grade C waste wood at our plants, we’re not just producing electricity, we’re reducing landfill waste and promoting a circular economy that benefits everyone.
By utilising materials like Grade C waste wood at our plants, we’re not just producing electricity, we’re reducing landfill waste and promoting a circular economy that benefits everyone.


